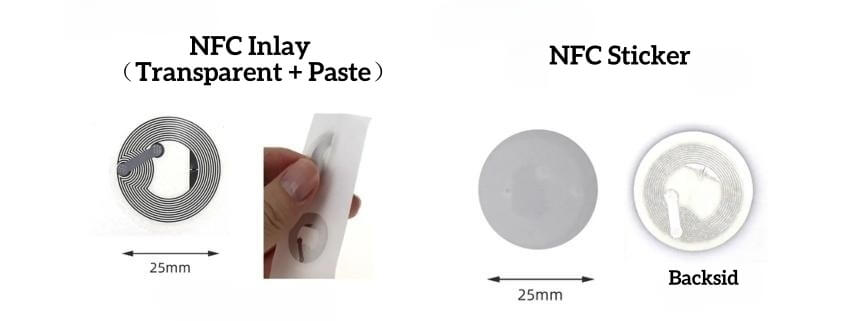
Brief Description of Ntag 213/215/216 Chip Differences and Application Areas
The NTAG 213/215/216 are all NFC (Near Field Communication) chips developed by NXP Semiconductors, a kind of High-Frequency 13.56MHz Chips. Each chip has specific characteristics and capabilities, making them suitable for different application areas. Let’s explore the differences and common application areas for each chip:
- NTAG 213:
- Memory Capacity: 144 bytes of user memory.
- Features: It is the most basic and cost-effective chip in the NTAG series.
- Application Areas:
- Access Control: Used for simple access control systems like door entry badges or authentication tokens.
- Product Authentication: Employed to verify the authenticity of products, particularly in anti-counterfeiting measures.
- Simple Data Exchange: Suitable for basic information exchange like URLs, contact details, or small amounts of data.
- NTAG 215:
- Memory Capacity: 504 bytes of user memory.
- Features: Larger memory compared to NTAG 213, enabling more data storage.
- Application Areas:
- Marketing and Advertising: Used in smart posters, business cards, or promotional items to store additional data like images, brochures, or longer URLs.
- Social Media Integration: Enables easy integration with social media platforms, allowing users to follow links or profiles.
- Gaming: Utilized in interactive gaming applications that require more data storage for game elements.

- NTAG 216:
- Memory Capacity: 888 bytes of user memory.
- Features: The largest memory capacity among the three, providing even more data storage.
- Application Areas:
- Public Transport Ticketing: Used in contactless ticketing systems for public transportation, where more data space may be required for ticket information.
- Advanced Product Authentication: Useful for applications demanding higher security and more extensive authentication data.
- NFC e-Coupons: Employed in electronic coupon systems that require additional information for redemption.

It’s important to note that all three NTAG chips are compatible with NFC-enabled smartphones and devices, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. The choice of the chip depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as the amount of data to store, the level of security needed, and the budget constraints.

